The Bladder, Ureter and UrethraThe physiology of the Bladder
The walls of the bladder are made from special cells that have the capacity both to stretch and contract.
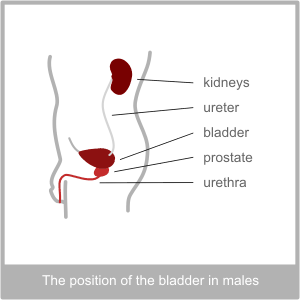
When the bladder is full (which in healthy adults usually means in contains around 300 millilitres of urine) nerve impulses stimulate it to contract. Through the first years of life we learn to override this impulse, which means that from then on this stage is simple recognised as the need to urinate.
The physiology of the Ureters
Urine flows steadily into the ureters. They receive between 20 – 100 millilitres an hour. This is propelled down the length of the ureter by steady muscular contractions within the cell walls. Urine is pushed into the bladder, through a structure which acts like a one way valve, in impulses about ever 10 seconds.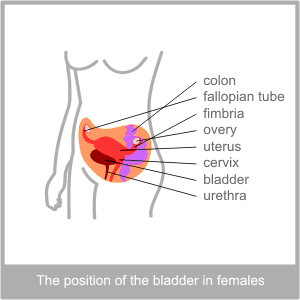
The physiology of the Urethra
The urethra links the bladder to the outside of the body. It passes through the floor of the pelvis (the perineum) and the pelvic floor muscles. In men the first part of the urethra also passes through the prostate gland.
Where the urethra meets the bladder there is a ring of muscle called the internal urethral sphincter which remains contracted until we want to urinate. This holds the urine in the bladder. The pelvic floor muscles also act as an external urethral sphincter to perform the same job.


